Introduction
In today’s fast-paced digital world, Quality Assurance (QA) engineers play a crucial role in ensuring that software applications are reliable, secure, and meet high-quality standards. As someone starting my journey in QA engineering, I’ve been researching how the field continues to evolve, particularly in 2025. This blog is my attempt to share insights I’ve gathered and reflect on the growing trends shaping the QA industry.
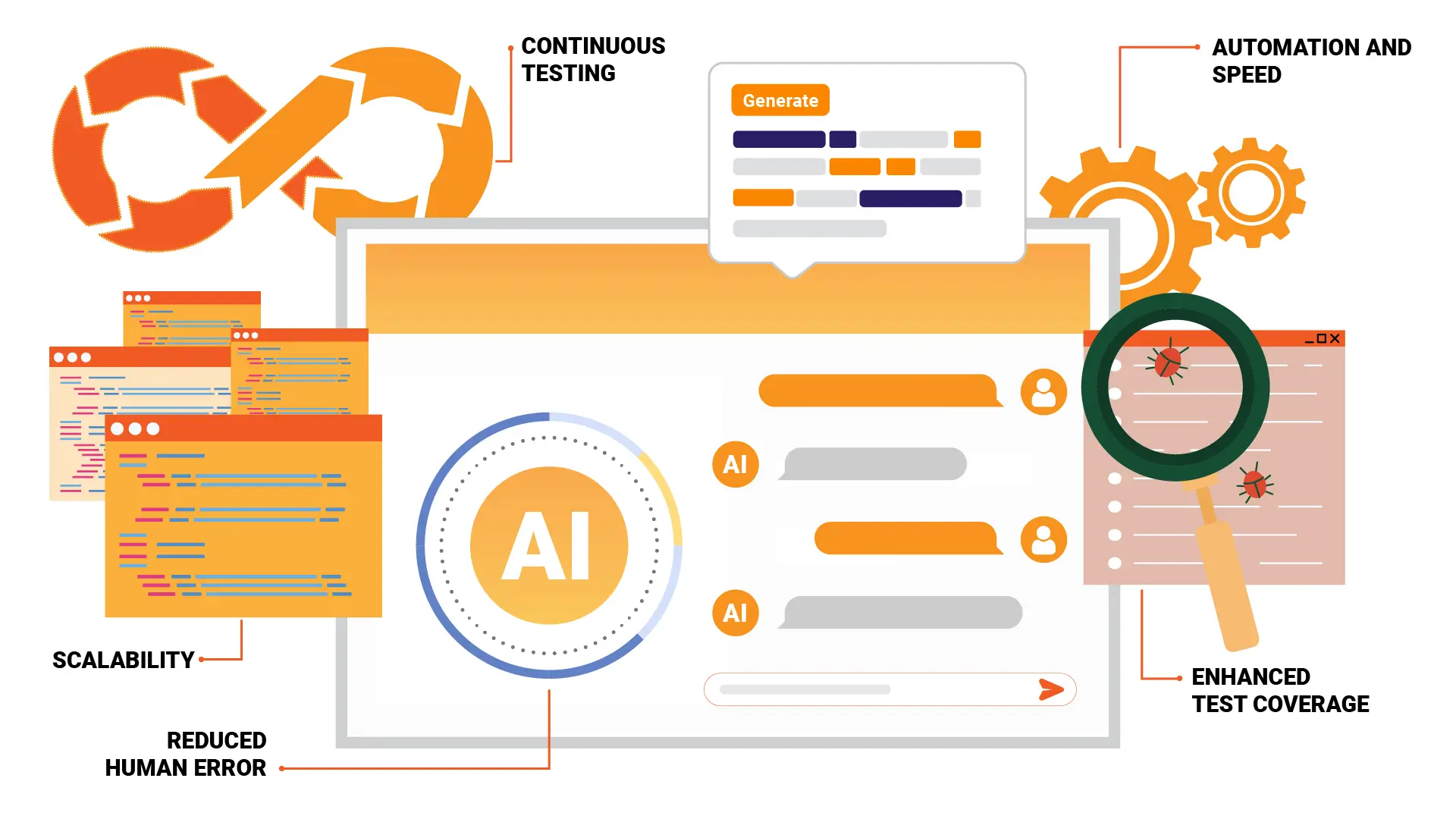
A key focus of my research has been on generative AI testing, an innovative approach that automates test case creation and identifies software issues using advanced AI algorithms. This technology offers incredible potential to efficiently detect bugs, security vulnerabilities, and performance issues, which are critical challenges for software teams.
Additionally, it’s clear that QA professionals need to deepen their understanding of DevOps practices, especially in continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines. This knowledge enables seamless collaboration with developers to ensure smoother feature deployments.
As cybersecurity threats become increasingly sophisticated, QA engineers must also stay updated on security testing methodologies, such as vulnerability assessments and penetration tests, to protect applications and user data.
Finally, with the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), the demand for robust testing of interconnected devices and virtual environments is growing. This makes IoT testing a critical skill for QA professionals.
This blog is not just a technical overview; it’s also a reflection of my own learning journey. By exploring these areas, I aim to understand how QA engineers can adapt to industry demands and thrive in this evolving field.
1. Continuous Learning
In 2025, QA engineers will need to be avid learners, constantly staying abreast of emerging technologies, new programming languages, and frameworks. This is crucial to adapt to the ever-changing software development landscape and ensure that QA processes align with the latest industry standards. Continuous learning will help QA engineers expand their knowledge, not only in traditional testing methodologies but also in emerging areas such as DevOps, cloud computing, and machine learning.
2. Learning about AI and Machine Learning
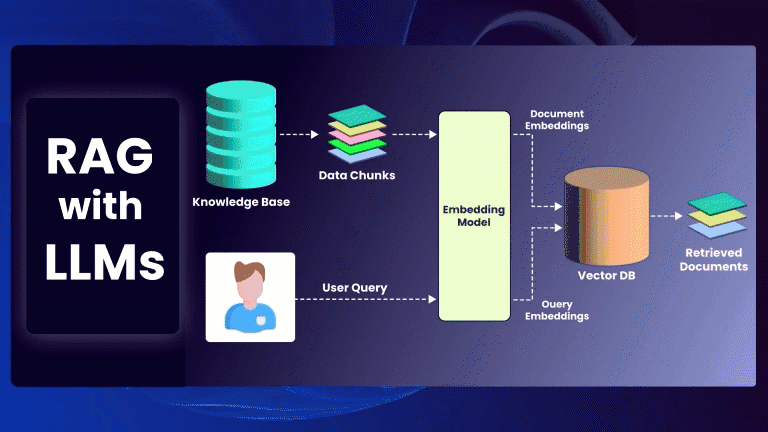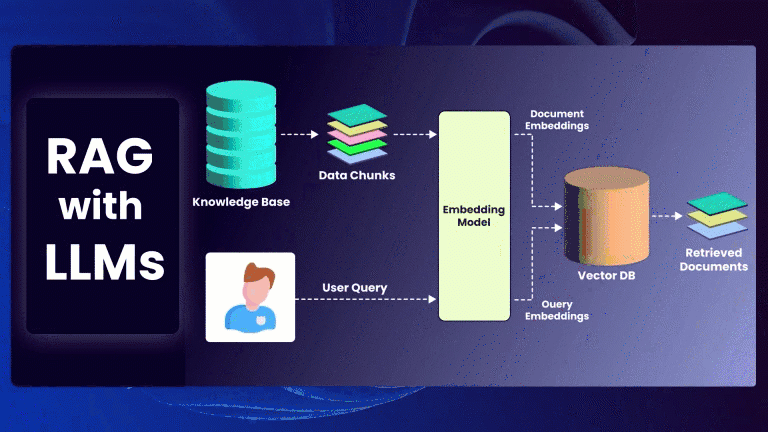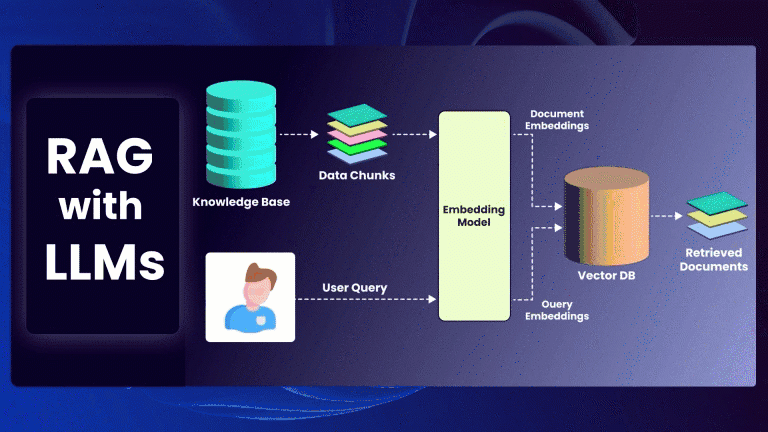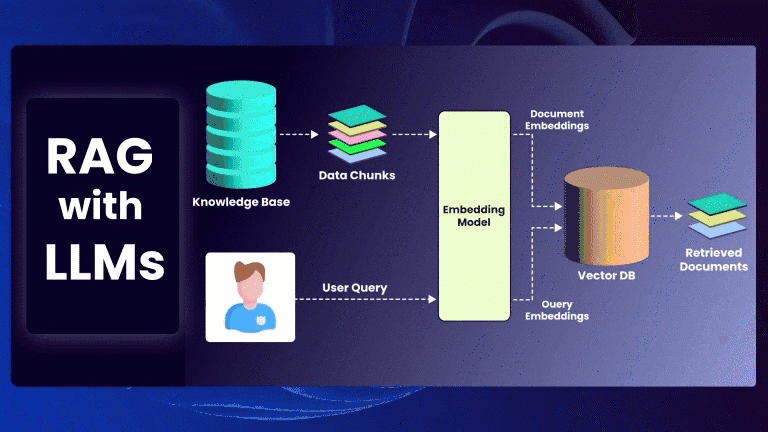
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are rapidly advancing in the field of software testing. QA engineers who are familiar with these technologies can benefit from optimized test case creation, improved defect identification, and faster test performance. It is important for QA engineers to have a basic understanding of AI and ML in order to fully comprehend the advantages of generative AI testing and effectively apply it in their testing methodologies. Knowing popular ML frameworks like TensorFlow or PyTorch will enable QA professionals to develop models that can autonomously generate test cases or predict potential defects.
3. Adopting Generative AI Testing
Generative AI testing involves using AI models to simulate user behavior and generate large volumes of test cases. This approach allows for extensive test coverage and aids in uncovering hidden bugs that traditional testing may miss. QA engineers should invest time in learning generative AI techniques and tools, as this approach promises to revolutionize the testing process by minimizing human effort and maximizing test efficiency.
4. Collaboration and Communication Skills
As QA engineers master emerging technologies and generative AI testing, collaboration and communication skills will be essential. They must work closely with developers and stakeholders to align testing with project goals. Additionally, they need to effectively communicate testing results, progress updates, and necessary improvements to the development team. In a highly collaborative and tech-driven environment, strong interpersonal skills are crucial.






good